Monitoring blood pressure is crucial for individuals with health conditions such as hypertension, diabetes, or cardiovascular disease. A sphygmomanometer for blood pressure monitoring remains the gold standard quality. Whether using an aneroid sphygmomanometer (manual) or a digital blood pressure monitor, understanding how to use it correctly ensures precise results and better management of your health.
This article explains the proper method to use a sphygmomanometer, its importance, and its impact on health and society, particularly in the Philippines’ context. We’ll also compare different methods and provide practical tips for accurate readings.
Monitoring blood pressure helps manage health conditions and prevent complications like stroke, heart attack, and kidney disease. Individuals with chronic illnesses must check their blood pressure regularly to ensure their treatment plan is effective.
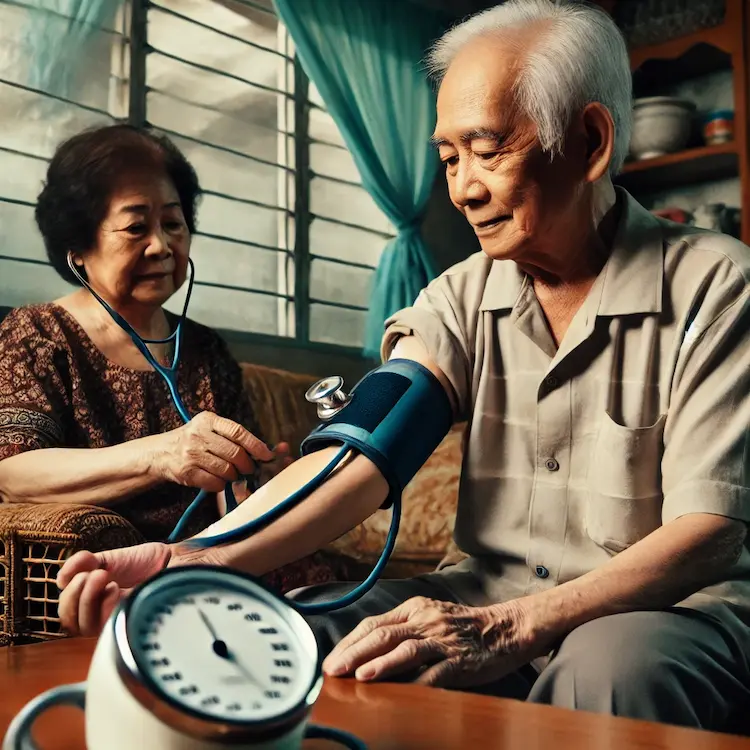

There are three main types of sphygmomanometers used in the Philippines:
| Type | Description | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mercury Sphygmomanometer | Traditional and most accurate | Highly precise | Bulky, contains mercury (toxic) |
| Aneroid Sphygmomanometer | Manual with a dial gauge | Affordable, portable | Requires training for accuracy |
| Digital Blood Pressure Monitor | Electronic and automated | Easy to use, best for home use | Less accurate if used incorrectly |
For individuals with health conditions, digital monitors are often preferred due to their ease of use. However, aneroid sphygmomanometers are still widely used in clinics and hospitals across the Philippines.
Follow these steps to ensure accurate blood pressure readings:
| Error | Impact on Reading | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Arm position too high or low | Incorrect pressure reading | Keep arm at heart level |
| Talking during measurement | Increased blood pressure | Stay silent and relaxed |
| Cuff too tight or loose | Unreliable results | Ensure proper cuff fit |
| Taking measurements too frequently | Fluctuating readings | Wait 1–2 minutes between readings |
For those with health conditions, the best times to check blood pressure are:
Aside from sphygmomanometer for blood pressure monitoring, other techniques exist for measuring blood pressure:
| Method | Description | Accuracy | Suitability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ambulatory BP Monitoring (ABPM) | 24-hour BP monitoring with a portable device | Very high | Ideal for those with fluctuating BP |
| Home Blood Pressure Monitoring (HBPM) | Regular monitoring at home using a digital sphyg | High | Convenient for self-monitoring |
| Clinic Measurements | BP taken at a doctor’s office | Moderate | May be affected by white coat syndrome |
In the Philippines, many hospitals and barangay health centers offer free blood pressure monitoring, making it easier for Filipinos to track their health.
Using a sphygmomanometer for blood pressure monitoring correctly is essential for managing health conditions effectively. Whether using a manual or digital monitor, following the right technique ensures accurate and reliable blood pressure readings. Given the high prevalence of hypertension in the Philippines, regular BP monitoring can help prevent complications and improve overall well-being.