Heart health is a critical aspect of overall well-being, and effective monitoring tools play a crucial role in maintaining it. Among these tools, sphygmomanometers, commonly known as blood pressure monitors, are essential for tracking cardiovascular health. Whether you’re managing hypertension, preventing heart disease, or simply keeping tabs on your health, a sphygmomanometer provides valuable insights into your heart’s condition.
This article explores the significance of sphygmomanometers, their impact on health and society, and how they compare to other heart health monitoring methods. We will also provide practical tips on choosing the right device and using it effectively.
Why Monitoring Blood Pressure Matters
Blood pressure is a key indicator of heart health. High blood pressure (hypertension) is a leading cause of cardiovascular disease, increasing the risk of stroke, heart attack, and kidney failure. On the other hand, low blood pressure (hypotension) can cause dizziness, fainting, and shock in extreme cases.
The Global Impact of Hypertension
- Over 1.28 billion adults worldwide suffer from hypertension, with two-thirds of them living in low- and middle-income countries (WHO, 2023).
- Hypertension is called the “silent killer” because many people remain undiagnosed until they experience serious complications.
- The economic burden of hypertension is significant, with billions spent annually on treatment and hospitalizations.
Regular monitoring with a sphygmomanometer allows early detection and management, preventing complications and improving quality of life.
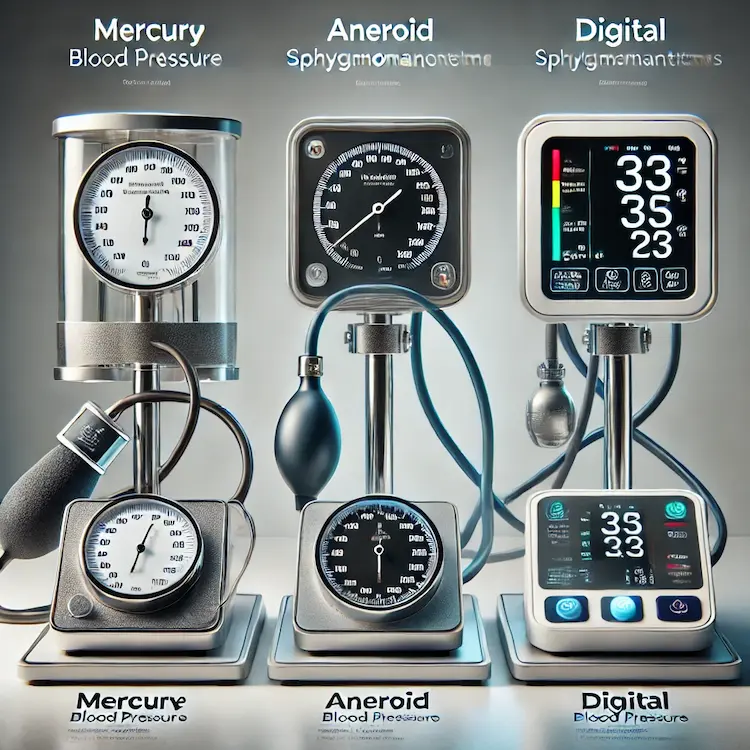
Types of Blood Pressure Monitors (Sphygmomanometers)
There are three primary types of sphygmomanometers, each with its advantages and limitations:
| Type |
Features |
Pros |
Cons |
| Mercury Sphygmomanometer |
It uses mercury to measure pressure. Requires a stethoscope. |
Highly accurate, long lifespan |
Bulky, risk of mercury exposure |
| Aneroid Sphygmomanometer |
Uses a dial gauge and a stethoscope. No mercury. |
Portable, durable |
Requires manual skill, prone to calibration errors |
| Digital Sphygmomanometer |
Uses electronic sensors. Fully automated. |
Easy to use, suitable for home monitoring |
Can be less accurate with improper use |
Which Type is Best for You?
- Clinics and hospitals often prefer mercury sphygmomanometers due to their accuracy.
- Doctors and nurses commonly use aneroid sphygmomanometers for portability and reliability.
- Home users benefit from digital monitors, which provide quick readings without medical expertise.
How Sphygmomanometers Compare to Other Heart Health Monitoring Tools
While blood pressure monitors are crucial, other devices also contribute to cardiovascular monitoring. Here’s how they compare:
| Device |
Function |
Use Case |
Key Benefit |
| Sphygmomanometer |
Measures blood pressure |
Home, clinics, hospitals |
Tracks hypertension, immediate readings |
| ECG (Electrocardiogram) |
Records heart’s electrical activity |
Hospitals, diagnostic centers |
Detects arrhythmias, heart attack risks |
| Pulse Oximeter |
Measures oxygen levels and pulse rate |
Home, hospitals |
Useful for detecting respiratory issues |
| Holter Monitor |
Tracks heart rhythm over 24+ hours |
Patients with suspected arrhythmias |
Provides long-term data for diagnosis |
A sphygmomanometer is the most accessible and frequently used tool for monitoring heart health. However, those with existing heart conditions may need additional tools like ECGs for comprehensive assessment.
How to Use a Sphygmomanometer Correctly for Accurate Readings
Improper use of a sphygmomanometer can lead to inaccurate readings. Follow these steps for precise measurements:
Step 1: Prepare for Measurement
- Sit in a quiet place, relax for 5 minutes before measurement.
- Avoid caffeine, smoking, and exercise for at least 30 minutes prior.
- Sit with your feet flat on the ground, back supported, and arm resting at heart level.
Step 2: Position the Cuff Correctly
- Wrap the cuff around your bare upper arm, about 1 inch above the elbow.
- Ensure the cuff is snug but not too tight—two fingers should fit under the cuff.
Step 3: Take the Reading
- If using a digital sphygmomanometer, press the start button and wait.
- For manual sphygmomanometers, inflate the cuff to 180 mmHg, then slowly release the air while listening with a stethoscope.
- Record systolic (top number) and diastolic (bottom number) pressure.
Step 4: Interpret the Results
- Normal: Below 120/80 mmHg
- Elevated: 120–129/less than 80 mmHg
- Hypertension Stage 1: 130–139/80–89 mmHg
- Hypertension Stage 2: 140+/90+ mmHg
- Crisis: 180+/120+ mmHg (Seek immediate medical attention)
Practical Tips for Managing Blood Pressure Effectively
Monitoring blood pressure is just one part of
heart health management. Here are practical tips to maintain a healthy heart:
Maintain a Heart-Healthy Diet
- Eat more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Limit sodium intake to less than 2,300 mg per day.
- Reduce processed foods and sugary drinks.
Exercise Regularly
- Aim for 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week (e.g., brisk walking, cycling).
- Strength training twice a week helps improve cardiovascular function.
Manage Stress
- Practice deep breathing, meditation, and mindfulness.
- Avoid excessive work stress and prioritize quality sleep (7–9 hours per night).
Limit Alcohol and Quit Smoking
- Excessive alcohol raises blood pressure; limit to one drink per day (women) or two (men).
- Smoking damages arteries and increases the risk of hypertension.
Monitor Blood Pressure at Home
- Check blood pressure at the same time daily.
- Keep a record of readings to track trends over time.
Conclusion
Sphygmomanometers are indispensable tools for managing heart health, providing crucial insights into blood pressure levels. With hypertension being a global health concern, regular monitoring enables early detection and proactive management. Whether using a mercury, aneroid, or digital sphygmomanometer, choosing the right tool and using it correctly ensures accurate results.
By combining blood pressure monitoring with a healthy lifestyle, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of cardiovascular disease and enjoy a longer, healthier life.
Key Takeaways
- Regular blood pressure monitoring helps prevent heart disease.
- Digital sphygmomanometers are ideal for home use, while mercury and aneroid types offer higher accuracy in clinical settings.
- Compare blood pressure readings with other heart health tools like ECGs for a complete cardiovascular assessment.
- Lifestyle changes, including diet, exercise, and stress management, are essential for long-term heart health.
Actionable Recommendations
- Invest in a reliable blood pressure monitor suited to your needs.
- Follow best practices for accurate readings (correct cuff placement, proper positioning).
- Consult a doctor if blood pressure remains consistently high.
- Adopt heart-healthy habits to prevent or manage hypertension.

