Obesity is a major global health concern, significantly increasing the risk of hypertension (high blood pressure) and cardiovascular diseases. Regular blood pressure monitoring is essential for early detection, management, and prevention of serious complications. Sphyg, a trusted supplier of medical equipment, provides clinically proven devices that help individuals effectively track and manage their blood pressure.
This article explores the link between Obesity and Hypertension, the importance of routine monitoring, different types of blood pressure monitors, and practical strategies for maintaining healthy levels.
Obesity contributes to high blood pressure through multiple physiological mechanisms:
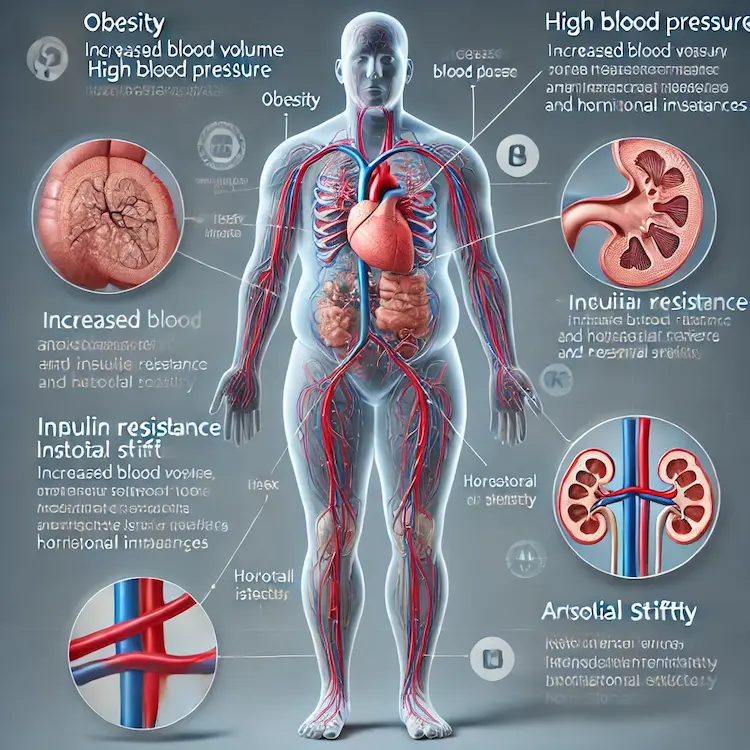
Chronic hypertension in obese individuals can cause severe health complications, including:
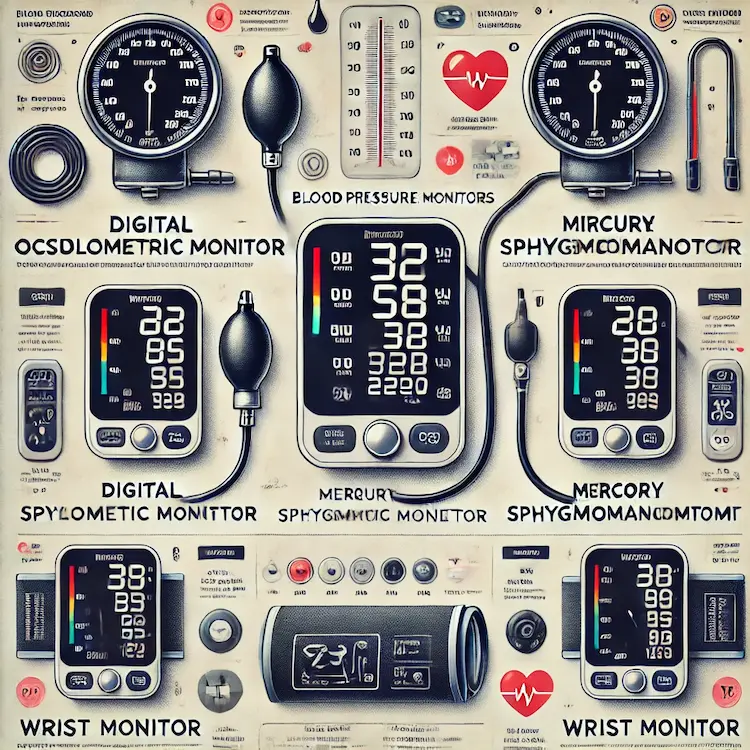
Choosing the right blood pressure monitor is crucial for accurate readings. Below is a comparison of different types of monitors:
| Type of Blood Pressure Monitor | Features | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oscillometric (Digital Monitors) | Uses electronic sensors to measure pressure | Easy to use, automatic, stores readings | May be slightly less accurate for irregular heartbeats |
| Mercury Sphygmomanometer | Traditional device using mercury for precise measurement | High accuracy, gold standard for professionals | Bulky, requires training, mercury exposure risk |
| Aneroid Sphygmomanometer | Uses a mechanical dial and stethoscope | Portable, accurate when used correctly | Requires skill, prone to human error |
| Wrist Blood Pressure Monitors | Measures pressure at the wrist, often digital | Convenient, compact, good for travel | Less accurate than arm monitors, affected by hand position |
| Finger Blood Pressure Monitors | Small device placed on a finger | Portable, easy to use | Least accurate, affected by movement and positioning |
To obtain accurate readings, follow these guidelines:
In addition to monitoring, lifestyle modifications are key to controlling hypertension in obese individuals.
Blood pressure monitoring is essential for individuals with obesity to prevent life-threatening complications such as heart disease and stroke. Devices like Sphyg’s clinically validated monitors offer a convenient and accurate way to track blood pressure at home. Along with routine monitoring, lifestyle changes like healthy eating, exercise, stress management, and medical supervision play a crucial role in maintaining optimal blood pressure levels.