Pregnancy is a transformative phase in a woman’s life, but it also comes with various health risks. One of the most critical concerns is blood pressure management, as high or low blood pressure can lead to complications for both the mother and the baby. Understanding the role of Sphyg (sphygmomanometer) in pregnancy monitoring is essential for ensuring a safe and healthy pregnancy.
This article delves into the importance of managing blood pressure during pregnancy, the potential health risks, methods of monitoring, and practical steps for maintaining optimal blood pressure. We also compare different monitoring tools, discuss societal implications, and provide actionable recommendations for expecting mothers.
Blood pressure monitoring plays a pivotal role in maternal and fetal health. Pregnancy induces significant physiological changes, impacting circulatory functions. Failure to regulate blood pressure can lead to serious complications, including preeclampsia, preterm birth, and fetal growth restrictions.
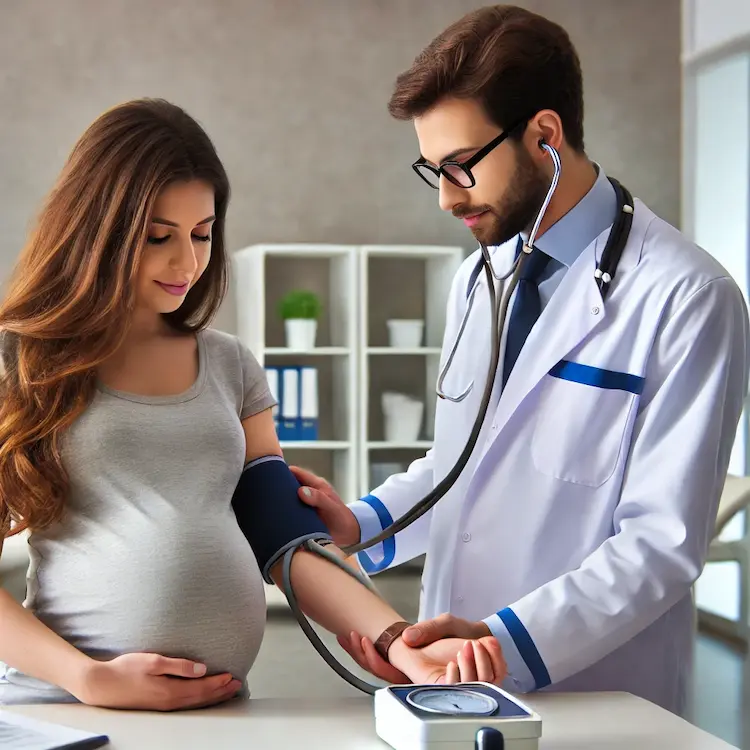

Pregnant women can experience various forms of blood pressure fluctuations, including:
If left unchecked, hypertension during pregnancy can lead to:
High maternal mortality rates, healthcare costs, and the long-term effects of premature birth make blood pressure management a public health concern. With over 10% of pregnancies affected by hypertension globally, raising awareness and access to accurate monitoring tools is crucial.
Blood pressure can be monitored using different devices, including manual sphygmomanometers, digital monitors, and ambulatory blood pressure monitoring (ABPM). Each method has its advantages and considerations.
| Method | Advantages | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Manual Sphygmomanometer | High accuracy, used by professionals | Requires expertise, not ideal for self-monitoring |
| Digital Blood Pressure Monitor | Easy to use, home-friendly, instant readings | May be less precise than manual methods |
| Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring (ABPM) | 24-hour monitoring, detects fluctuations | Expensive, typically used for high-risk cases |
For pregnant women, digital monitors with automatic cuff inflation are ideal for daily home monitoring. However, periodic manual readings by healthcare professionals provide better accuracy and validation.
Apart from monitoring, managing blood pressure effectively requires a multi-faceted approach. Below is a comparison of medical interventions, lifestyle changes, and natural remedies.
| Approach | How It Works | Effectiveness & Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Medications (Prescribed by a Doctor) | Used for severe cases of hypertension | Highly effective, but some may have side effects |
| Dietary Changes | Reducing sodium, increasing potassium, and eating whole foods | Essential for maintaining stable blood pressure |
| Exercise & Physical Activity | Walking, prenatal yoga, and light workouts | Helps improve circulation, should be done under guidance |
| Stress Management Techniques | Meditation, deep breathing, and adequate sleep | Reduces cortisol levels, indirectly stabilizing BP |
| Hydration & Fluid Intake | Drinking enough water supports cardiovascular function | Simple yet effective for maintaining healthy circulation |
To ensure healthy blood pressure levels throughout pregnancy, follow these key steps:
Blood pressure management during pregnancy is a critical aspect of maternal and fetal health. Regular monitoring using Sphyg devices, combined with lifestyle modifications and medical interventions, significantly reduces the risk of complications. As hypertension in pregnancy is a growing global health issue, raising awareness and promoting accessible solutions can improve maternal and infant outcomes.