Sphygmomanometers, commonly known as blood pressure monitors, are essential medical devices used to measure arterial blood pressure. These instruments play a crucial role in diagnosing and managing hypertension, a major risk factor for cardiovascular diseases. This article explores the various types of sphygmomanometers, their features, advantages, and limitations.
Mercury sphygmomanometers have long been considered the gold standard for blood pressure measurement due to their accuracy and reliability. These devices consist of a mercury-filled column connected to an inflatable cuff. As the cuff is inflated and deflated, the mercury level in the column rises and falls, allowing for precise readings.
Despite their accuracy, mercury sphygmomanometers are being phased out in many countries due to environmental concerns related to mercury toxicity. Their use is now primarily limited to clinical research and calibration of other devices.
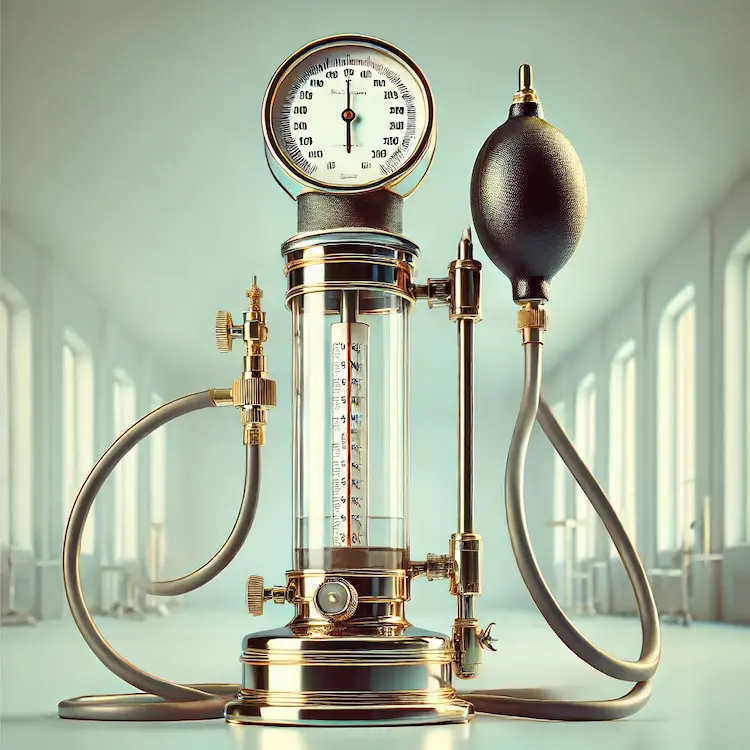

Aneroid sphygmomanometers are mechanical devices that use a metal bellows and lever system instead of mercury. They are widely used in clinical settings due to their portability and mercury-free design.
While aneroid devices are generally accurate when properly maintained, they are more susceptible to calibration errors due to mechanical wear and physical shocks. Regular calibration checks are essential to ensure accurate readings.
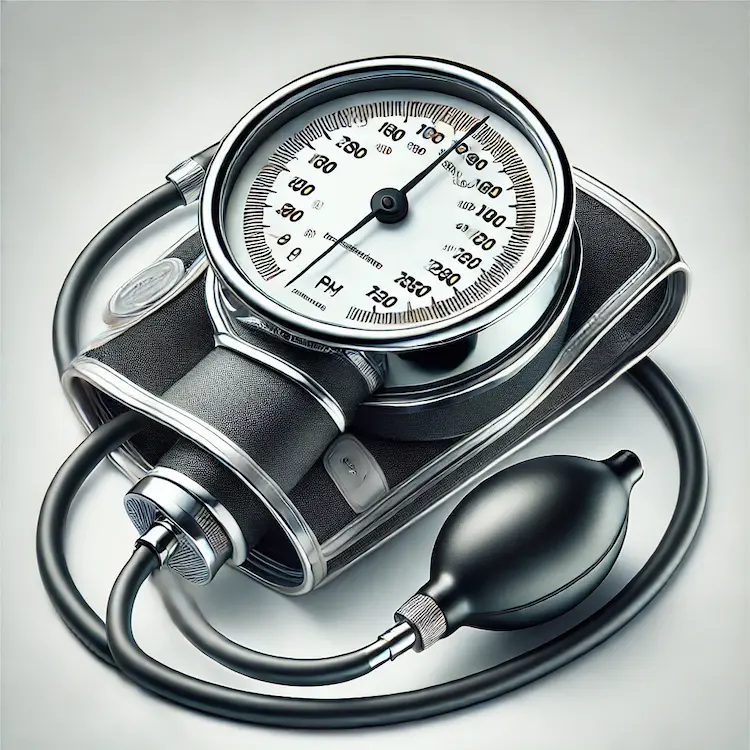

Digital sphygmomanometers have gained popularity in both clinical and home settings due to their ease of use and automated measurements. These devices use oscillometric technology to detect blood flow and calculate blood pressure.
Digital devices are particularly useful for home blood pressure monitoring, as they require minimal training to operate. However, their accuracy can be affected by factors such as movement, irregular heart rhythms, and cuff positioning.
| Feature | Mercury | Aneroid | Digital |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Highest | High (when calibrated) | Good |
| Ease of use | Requires training | Requires some skill | Easiest |
| Portability | Low | High | High |
| Maintenance | Minimal | Regular calibration | Battery replacement |
| Environmental concerns | High (mercury) | Low | Low |
| Cost | High | Moderate | Varies |
The accuracy of blood pressure measurements is crucial for proper diagnosis and management of hypertension. Studies have shown that aneroid devices, when properly maintained, can provide measurements comparable to mercury sphygmomanometers.
In one study, 283 aneroid devices were tested, and 100% were found to be accurate within the range recommended by the Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation. However, the accuracy of aneroid devices can deteriorate over time, especially if not regularly calibrated.
Digital sphygmomanometers have shown varying levels of accuracy in different studies. While many are clinically validated and provide reliable measurements, some may be less accurate than mercury or well-calibrated aneroid devices.
Regardless of the type of sphygmomanometer used, proper measurement technique is crucial for accurate blood pressure readings. Key factors include:
Healthcare professionals should be trained in proper blood pressure measurement techniques to ensure accurate and consistent results across different devices.
The shift away from mercury sphygmomanometers is primarily driven by environmental concerns. Mercury is a toxic substance that can pose risks to human health and the environment if not properly handled and disposed of.
Aneroid and digital sphygmomanometers offer mercury-free alternatives, aligning with global efforts to reduce mercury use in medical devices. However, it’s important to note that these devices may have their own environmental impacts, such as battery disposal for digital models.
The field of blood pressure measurement continues to evolve, with new technologies emerging to improve accuracy and convenience. Some notable trends include:
These innovations aim to make blood pressure monitoring more accessible and integrated into daily life, potentially improving hypertension management and cardiovascular health outcomes.
Sphygmomanometers play a vital role in healthcare, and the choice between mercury, aneroid, and digital devices depends on various factors including accuracy requirements, ease of use, and environmental considerations. While mercury devices remain the gold standard, well-maintained aneroid sphygmomanometers and validated digital devices offer reliable alternatives for clinical and home use.
Healthcare providers should be aware of the strengths and limitations of each type of sphygmomanometer and ensure proper technique and regular device maintenance to obtain accurate blood pressure measurements. As technology advances, new innovations in blood pressure monitoring may further improve our ability to manage hypertension and reduce cardiovascular risks.